
-
Soybean Diseases
- Asian Rust
- Anthracnose
- Bacterial Blight
- Bacterial Pustule
- Bean Pod Mottle Virus
- Brown Stem Rot
- Cercospora Leaf Blight
- Charcoal Rot
- Downy Mildew
- Frogeye Leaf Spot
- Green Stem Syndrome
- Iron Deficiency Chlorosis
- Phytophthora Root & Stem Rot
- Powdery Mildew
- Rhizoctonia
- Seedling Diseases
- Septoria (Brown Spot)
- SCN (Soybean Cyst Nematode)
- Soybean Mosaic Virus
- Stem Canker
- Sudden Death Syndrome
- Viruses
- White Mold
- Soybean Pests
- Diagnostic Help
- Field Trials
- Soybean Library
Your Soybean Checkoff.
Delivering Results.
Illinois
Indiana
Iowa
Kansas
Michigan
Minnesota
Missouri
Nebraska
North Dakota
Ohio
South Dakota
Wisconsin
Soybean Growth Stages
 |
 |
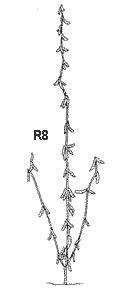 |
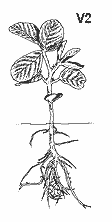
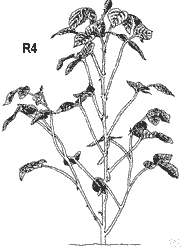
| V2 Two nodes on the main stem with fully developed leaves. | R4 Pod is 3/4" long at one of the four uppermost nodes on the main stem with a fully developed leaf. | R8 Ninety-five percent of the pods have reached their mature pod color. |
Vegetative stages
| VE | Emergence | Emergence of young plants through the soil surface with cotyledons (seed leaves) above the soil |
| VC | Cotyledon | The plant has emerged and cotyledons are fully unfolded |
| V1 | first node | The first node appears and the unifoliate leaves are fully developed opposite each other |
| V2 | 2 nodes | Two nodes on the main stem with fully developed leaves |
| V5 | 5 nodes | Counting the unifoliate node, there are four more nodes with fully developed trifoliolate leaves. Vegetative stages V6, V7... Vn continue until the first flower appears. Some varieties may accumulate as many as 20 nodes during the vegetative growth stage. |
Reproductive Stages
| R1 | Beginning flower | Open flower at any node on the main stem |
| R2 | Full flower | Open flower at one of the two uppermost nodes on the main stem |
| R3 | Beginning pod | Pod is 5 mm (3/16 inch) long at one of the four uppermost nodes on the main stem. |
| R4 | Full pod | Pod is 3/4" long at one of the four uppermost nodes on the main stem with a fully developed leaf. |
| R5 | Beginning seed | Seed is 1/8" long in a pod at one of the four uppermost nodes on the main stem. |
| R6 | Full seed | A pod containing a green seed that fills the pod cavity is located at one of the four uppermost main stem nodes. |
| R7 | Beginning maturity | One normal pod on the main stem has reached its mature pod color. |
| R8 | Full maturity | Ninety-five percent of the pods have reached their mature pod color. |
Sources
Stage of development descriptions for soybeans, glycine max. (L). Merrill.
Fehr & Caviness et al. Crop Science 11: 929-931 (1971).
Soybean Growth and Development (ISU PM 1943)
A 28-page publication that explains soybean growth and development through the life cycle of a maturity group II variety. Iowa State University Extension Distribution Center (Tel: 515- 294-5247)
Identifying Soybean Growth Stages. One-page, color illustrations (pdf file). Michigan State University.
Drawings courtesy of Anne E. Dorrance and Patrick E. Lipps.Profitable Soybean Disease Management in Ohio . Bulletin 895. Ohio State University.
